Program Control#
Problem#

Fig. 2 25 Oct. 1969 - Commander of the Apollo 12 lunar landing mission, sits in the cockpit of a Lunar Landing Training Vehicle (LLTV) during a lunar simulation flight at Ellington Air Force Base.
Public domain. By NASA Johnson Space Center. Source: Wikimedia Commons#
Various control systems#
Mechanical ⚙️#

Fig. 3 Steam engine using a centrifugal governor
CC BY-SA 3.0. By Panther. Source: Wikimedia Commons#
Electronic 💻#

Fig. 4 A chip on an Arduino board
Public domain. By DustyDingo. Source: Wikimedia Commons#
Manual 🤹🏼#
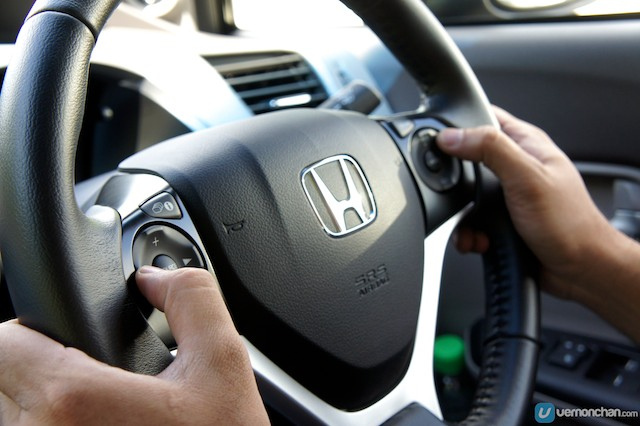

Fig. 5
CC BY 2.0. By Vernon Chan. Source: Wikimedia Commons#
Type |
Pro 👍 |
Con 👎 |
|---|---|---|
Mechanical ⚙️ |
simple, reliable |
bulky, complex systems not feasible |
Electronic 💻 |
flexibility through programmability (computers), small |
complex, reliability |
Manual 🤹 |
very flexible, can cope with an unknown environment |
costly, unreliable for repetitive tasks |
Regardless of the method, we use electronics to connect all systems together
Exercise 2
As an engineer in the R&D department of the space agency you are designing the following subsystems of a lunar lander:
a sensor for pointing the antenna to the world 📡
subsystem for traveling from space to moon’s proximity
subsystem for landing on the moon 🛬
For these scenarios:
pick one control method
explain with an example how electronics (and computers) can help in this scenario
Steps:
~1 min individually
~2 min compare with your partner
Deliverable: Write down your result and keywords for explanation
Assumption: We use a programmable electronic system to solve our problem.
Mission: Safe landing#
Fig. 6 Lunar lander trying to land#
Problems:
limited fuel 🌡️
crash if high speed 💥
How do we control ❓
Flowcharts#
Warning
We are repetitively running the program, i.e., if we are at the bottom, we come back to the beginning.
Exercise 3
Draw a flowchart for the following program
if the altitude is higher than 100
the thruster must be off.
if the altitude is lower than or equal 100
turn on the thruster
if the altitude lower than or equal 0 (landing)
the thruster must be off.
Steps:
~2 min individually
~1 min compare with your partner
Program control syntax#
General:
if (question1) {
action1;
} else if (question2) {
action2;
} else {
action3;
}
Question examples:
is the time 1?
time == 1
is the temperature lower or equal 20?
temperature <= 20
Action examples:
set the speed to 10
speed = 10
In words:
if
temperatureis greater than 30 then activateair_conditionerelse if
temperaturegreater than 25 activateventilatorelse turn everything off.
In code:
if (temperature > 30) {
air_conditioner = 1;
} else if (temperature > 25) {
ventilator = 1;
} else {
air_conditioner = 0;
ventilator = 0;
}
Exercise 4
Write code for landing using the following flowchart
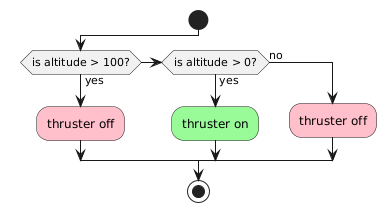
using the following independent lines:
} else {
} else if (altitude > 0) {
if (altitude > 0) {
thruster = 1;
thruster = 0;
thruster = 0;
}
Steps:
Work ~2 min individually. The program automatically tests your code.
Compare your result with your neighbor and help them.
Appendix#
In a programmable computer, program is programmed into the memory and executed by the computer.
![@startuml
package "Programmable computer" {
[processor] as cpu
[memory\n- ADD x1, x2\n- LOAD x3 ... (program)] as mem
mem --> cpu : read
cpu --> mem : write
}
@enduml](_images/plantuml-84b798f27ba8b2e1964406c51e020965503e5642.png)
